
In February 2025, Niccolo de Masi became CEO of IonQ, since when the company has been engaged in a hurricane of activity, including fund raisings, joint ventures, acquisitions and multiple new hirings. The company has raised over $3bn, including what it describes as the largest ($2bn) equity issue ever for a quantum computing company.
I don’t know if before de Masi, IonQ was virtually a one-man band, but it has an increasingly impressive top management team able to push the group in multiple directions.
IonQ is a bit like an early-stage pharmaceutical company with one important difference. Drug companies have no idea whether their fledgling drugs will make it to the commercial stage, but quantum computing is virtually certain to become a blockbuster product.
Share prices in the sector have exploded, leading to talk of a bubble. Look through sceptical eyes and you can see bubbles all over the place. Another possibility is that, almost overnight, quantum computing has gone from a pipedream to being a serious prospect. What remains uncertain is the timeline, but as long as the ultimate destination remains in view, that may not matter.
The prize is worth the effort.
Organizations that use the power of quantum computing could help humanity solve some of the world’s biggest problems and make breakthroughs in critical areas, from drug research to global agriculture and beyond.
As of 2025, quantum computing is in an experimental phase as the industry is still learning how to implement it on a mass scale. Companies such as Google, IBM and Microsoft are experimenting with this new technology to understand its potential uses. Data center admins should stay up to date with quantum computing as they will inevitably have to adapt to it.
Potential uses for quantum computing
Classical computing processes data in a binary space, which limits the volume of data it can handle and the decisions it can produce. This is also known as serial processing. Quantum computing, however, uses multidimensional processing.
Serial processing checks every combination of that data one at a time to arrive at the correct result. Multidimensional processing is layered, unlike the binary approach of serial processing, which uses bits. This accelerates the delivery and accuracy of computations and enhances the diversity of the results, which means that quantum computing can deliver better quality results faster.
Below are seven practical applications of quantum computing that are foreseeable with future technological development.
AI and machine learning
The capability of calculating solutions to problems simultaneously, as opposed to sequentially, has huge potential for AI and machine learning (ML). Organizations today use AI and ML to discover ways to automate and optimize tasks. Optimization can happen much faster and at scale when combined with quantum computing, especially when processing and analyzing highly complex or even unstructured big data sets.
Financial modeling
With the modeling capabilities of quantum computing, financial organizations could use the technology to better model the behavior of investments and securities at scale. This could help reduce risk, optimize large-scale portfolios and help financial organizations better understand the trends and movements of the global financial economy.
Cybersecurity
Quantum computing could have a direct affect on privacy and encryption. Given the rapidly evolving nature of the cybersecurity landscape, quantum computers could help keep data encrypted while in use, providing both in-transit and at-rest protection.
Route and traffic optimization
Optimal route planning is key to smooth supply chain logistics and transportation. The biggest challenge is harnessing all the real-time data — from changing weather patterns to traffic flow — that affects this planning. This is where quantum computers can excel. They could process all that data in real time and adjust routes for an entire fleet of vehicles simultaneously, putting each on the optimal path forward.
Manufacturing
Quantum computers can run more accurate and realistic prototyping and testing. In the manufacturing space, this could help reduce the cost of prototyping and result in better designs that don’t need as much testing.
Drug and chemical research
Quantum computers can create better models for how atoms interact with one another, leading to a superior and more precise understanding of molecular structure. This might directly affect drug and chemical research and how new products and medicines are developed. The predictive power of quantum computers could also provide foresight into how chemical compounds and drugs would develop, evolve and interact with other elements over time.
Batteries
Quantum computing could help manufacturers better understand how to incorporate new materials into products such as batteries and semiconductors. This could provide more insight into optimizing batteries for longevity and efficiency. Quantum computing can also help manufacturers better understand lithium compounds and battery chemistry. For example, quantum computing could tap into how the docking energy of proteins works, which results in better batteries for electric vehicles.
A future powered by quantum computing holds great promise, enabling the ability to tackle some of humanity’s most significant challenges more quickly, efficiently, accurately and on a larger scale.
Informa, 27 January 2025
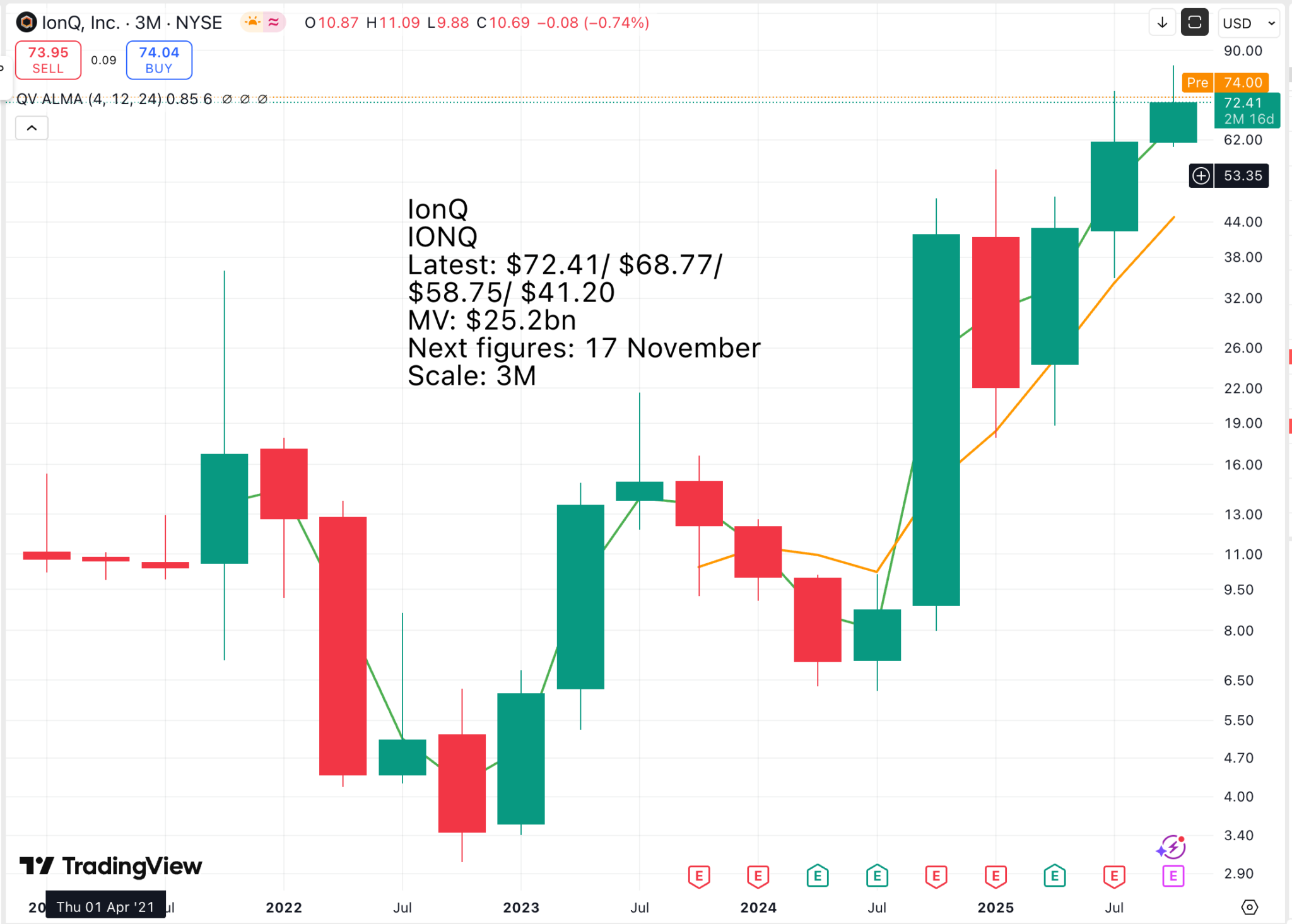
This chart is classic ‘Rubbish Theory of Value’. In little over a year, the shares fell from $36 to $3 before rebounding. Traditional valuation techniques don’t work for shares like IonQ, which are priced on newsflow and progress towards a distant but incredibly exciting goal.
What would IonQ be worth today if we knew that a decade from now, the company’s technology was being used to solve problems like those described above? We live in a world with an insatiable demand for ever more staggering computing power able to process gigantic streams of data and spew out intelligence, solutions and answers.
Maybe data is the key. Back in the day, computers had little to feed on. Still, the Internet and then the cloud provide an inexhaustible and ever-growing tsunami of material, enabling humanity to address ever more staggering problems and ask ever more complex questions.
How much data and how much computing power will be needed to solve problems like the origins of life? As Moore’s Law becomes a distant memory, new techniques are needed, which will require investment on a colossal scale and, for the moment at least, the input of countless brainy humans.
IonQ and other shares like it are not so much investments as bets which could deliver giant payoffs sometime in the future. What investors want to see is a sense of purpose, diligent management of the finances and progress. IonQ looks set to deliver all those things.
Share Recommendations
IonQ IONQ
Below are a few snippets highlighting why IonQ appears to be an exciting investment.
IonQ is experiencing incredible momentum, and I’ve never been more confident in our potential as we have look ahead.
Niccolo McCleod Di Masi, CEO, IonQ, Q2 2025, 6 August 2025
There is so much going on.
This quarter, we significantly expanded our global footprint, solidifying our role as the partner of choice by countries building their quantum economies. We signed an MOU designed to advance quantum computing in Japan with AIST’s G-QuAT, the country’s premier R&D center for quantum and AI. We were also recently named the primary quantum partner by South Korea’s KISTI Institute to build their National Quantum Center of Excellence. In the U.S., we announced a $22 million deal to build the first commercial quantum computing and networking hub in America with EPB, a pioneering power and telecommunications company. Additionally, our partnership with the U.S. government continues with our selection by DARPA to help inform quantum industry standards.
Beyond building these ecosystem partnerships, we are proving our value on critical commercial applications. For example, we launched a world-first collaboration with AstraZeneca, AWS and NVIDIA that demonstrated a 20x performance speed up for a
key drug development workflow, showcasing practical quantum advantage. IonQ is also tackling critical national energy issues in partnership with Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the U.S. Department of Energy. We have developed a new hybrid quantum classical computing approach that helps determine the optimal schedule for power generators to meet electricity demand at minimal cost. This accomplishment establishes a clear path for our systems to address the staggering 60% of energy currently lost due to grid inefficiencies.
Niccolo McCleod Di Masi, CEO, IonQ, Q2 2025, 6 August 2025
The company is moving fast on the acquisition front to build a leadership position in Quantum Computing.
By our acquisition of Lightsynq and planned acquisition of Oxford Ionics, we have created the most advanced, accelerated and powerful quantum computing road map in the world. As we outlined on our webinar on June 9, we believe the combination of IonQ hardware and software prowess, Oxford’s implementation of an ion trap on a chip provides the team, IP technology momentum to achieve 800 logical qubits in 2027 and 80,000 logical qubits in 2030. We already have a manufacturing center in Seattle and with the anticipated addition of Oxford Ionics in the U.K., we have an additional site to expand both core computing R&D and manufacturing for EMEA.
We also announced the close of our acquisition of Capella in July, representing a significant step forward in recognizing our vision of a space-based quantum key distribution network. Frank Backes, CEO of Capella, will speak to this in more detail shortly. All of my colleagues, both veteran and new, are tremendously excited about the power of our talent density and combined capabilities. There is room for upside in our road map as we continue to integrate and operationalize our technologies. But best of all is a truly fantastic combination of low bill of material costs and near limitless extensibility. These attributes of IonQ’s quantum computing approach are protected by over 1,000 patents and patents pending, ensuring winning unit economics at every stage of the quantum revolution.
Our road map assumes Oxford Ionics can reach 2 million qubits per chip. However, our ambitions are to continue increasing ion density and driving down costs on Oxford Ionics chips to someday have 10 million ion traps on a single chip. Then using IonQ’s modular scaling approach, we will break the single processor barrier. By connecting 2 quantum processors via Lightsynq photonic interconnect technology, we plan to scale to tens of millions of logical qubits and deliver immense computational power.
Niccolo McCleod Di Masi, CEO, IonQ, Q2 2025, 6 August 2025
The company is collecting an impressive array of talent.
Moving on now to talent. I’ll begin with the wonderful news that our Co-Founder, Dr. Chris Monroe, has assumed the role of Chief Scientific Advisor. He holds the current world record for remote entanglement generation and trapped ion technology, an achievement that opens the door to scalable quantum networks. He’ll be spending significant time with our other world record holder in this area, Dr. Mihir Bhaskar, former CEO and Co-Founder of Lightsynq. Dr. Monroe, of course, also previously held a world record for qubit fidelity, a record currently held by Dr. Chris Ballance at Oxford Ionics. It’s, of course, both exciting and delightful that IonQ now
has world record holders in all our key scaling vectors collaborating on a daily basis to accelerate our momentum towards full fault tolerance.
On the networking side, we’re also very pleased that ID Quantique’s founder, Dr. Gregoire Ribordy, will remain in his role post close to continue building on his 20 years of leadership in Quantum Networking. Based in our Geneva office, Dr. Ribordy is a giant of the QKD space and has been shipping ever more impressive generations of his quantum networking equipment for over a decade now. World-renowned quantum researcher and industry figure, Dr. Marco Pistoia, joined us from JPMorgan Chase, where he previously ran all technology research at the biggest bank in the world. Dr. Pistoia is uniquely able to support our global efforts in financial services from both quantum computing and networking perspectives.
Dr. Rick Muller has joined us to head up Quantum Computing Systems development. As many of you know, Dr. Muller was formerly the Director of IARPA, our nation’s Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity organization, which is tasked with leading high- risk, high payoff research for the intelligence community. Dr. Muller is also a distinguished researcher originally from Caltech with over 20 years of experience at Sandia National Labs.
Finally, I’m excited that Paul Dacier has joined the company as Chief Legal Officer and Corporate Secretary for IonQ. For over 26 years, Paul was the General Counsel of EMC Corporation, where he was instrumental in driving significant growth for the company. During his tenure, revenue grew from $170 million to $25 billion in 2016. Employees grew from 750 to 68,000, and the company’s market cap grew from $100 million to $55 billion.
As I’ve said before, I believe talent is the proverbial Warren Buffett weighing machine, most relevant to any company’s long-term prospects. It’s tremendously validating and an outstanding vote of confidence in IonQ’s progress to have such towering world-class talent depart from highly respected roles to become our colleagues at IonQ. With the support of our market-making talent, our customer ecosystem continues to grow as we build the world’s leading quantum computing and networking offerings. We expect to drive our long-term success from our ability to land and expand with both our computing and networking solutions.
As a final comment, with the strongest balance sheet thus far in IonQ history [even before the latest $2bn fund raising], we have the ability to continue leading, pioneering and growing our ecosystem in both quantum computing and quantum networking worldwide.
Niccolo McCleod Di Masi, CEO, IonQ, Q2 2025, 6 August 2025
Networking is another area of intense activity.
IonQ is the only company building the quantum Internet at commercial scale. We are working with customers to bring all forms of quantum edge devices onto our quantum networks from security endpoints to quantum computers. IonQ customers will soon be able to cluster quantum computers for extremely powerful
processing, send ultra secure data from one quantum computer to another and seamlessly transmit data from quantum sensors to quantum computers.
A key milestone in this road map is our ability to build quantum networks over standard telecom fiber, which requires technology to convert wavelengths from these quantum devices to wavelengths compatible with classical networks. We are working on that technology with customers today and expect to be the first company in the world to achieve it. Across all dimensions, the infrastructure for the quantum Internet is being built here at IonQ.
Jordan Shapiro, president and general manager of Quantum Networking, IonQ, Q2 2025, 6 August 2025
The problem for investors is that, for all this activity in terms of reported numbers, IonQ is a tiny business with Q2 2025 sales of $20.7m and an EBITDA loss (similar to operating results) of $36.5m. If you want to buy the shares, you must forget about that and focus on the strong finances, the talent and the progress being made.
Di Masi loses me when he talks about the future, but he makes it sound exciting.
As you’ve seen throughout the compute space from CPUs to GPUs to now our QPUs, much of the upside and value comes from problems that you haven’t thought of addressing yet. And it comes as you start solving problems with ever more doubly exponentially powerful machines as IonQ has. So I think there’s tremendous upside in the app road map from quantum AI and quantum machine learning in particular. We’ve already made some industrial AI applications as far back as World Quantum Day on April 13, 14 earlier this year. We’re continuing to make progress with a number of partners, not just in the AI space, but of course, in the drug discovery space. You saw announcements from us on protein folding as well as with AstraZeneca.
You’ve seen announcements with partners looking at the energy grid and optimizations there. And of course, we work closely with the Electric Power Board of Tennessee and Oak Ridge National Labs already. So I think it’s safe to say that we’ve got a commanding lead in solving useful applications today even on just 36 qubit systems. Imagine where we’re going to be in the next year, 1.5 years, 2 years as we move to 256 qubits and at some point soon, 10,000 physical qubits in combination with our friends at Oxford Ionics. It unlocks a whole world of value add for every industry category we’re in already today.
We think that you can start to do useful Shor’s algorithm work probably in the 2027 time horizon, if you look at our road map, low thousands of logical qubits starts to become interesting for us on the encryption cracking front. The traveling sales sourcing problem, I believe, is about 1,000 logical qubits as well. And so a lot of work in logistics optimizations will get unlocked in the next 18 months or so. Our app team is growing as quickly as we can find the talent. We recognize that it’s a unique set of skills to be able to run quantum applications on our machines and then translate those for each of the verticals that have slightly different problems that we’ve gone after. But as I mentioned in my prepared remarks, it’s a key investment area for us. So we recognize that the path for growth for us goes right through our applications in all these different areas.
[Shor’s algorithm is a groundbreaking quantum algorithm developed by Peter Shor in 1994 that efficiently finds the prime factors of large integers, a task that is extremely difficult for classical computers. It provides an exponential speedup, making it a prime example of how quantum computers can solve certain problems much faster than their classical counterparts. This algorithm has significant implications for public-key cryptography, particularly RSA encryption, which relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers for its security.]
[The traveling salesman problem (TSP) is an optimization problem that asks for the shortest possible route to visit a given set of cities exactly once, starting from a central location and returning to the starting point. It is a classic problem in computer science and operations research, important for applications like logistics, where finding an efficient route is critical. The challenge lies in the fact that the number of possible routes grows so quickly with the number of cities that brute-force calculation becomes impossible for large numbers of cities.]
Niccolo McCleod Di Masi, CEO, IonQ, Q2 2025, 6 August 2025
What I like about Di Masi is that he conveys a sense of excitement, a priceless gift in a CEO who wants to do deals, attract talent, raise funding and motivate the team.
If you look at the acquisitions we made and the talent we’ve attracted, you can see that we are investing on both sides of the house to do exactly what I said. We want to make sure we always have the leading technical road map, the best unit economics and to make sure we continue to win market share. And we’ll continue to invest to achieve all 3 or 4 of those objectives. I’ve been delighted with every acquisition that we’ve consummated since I assumed this position, and I’ve been really delighted with the acceleration in global technical talent and talent in general that we’ve been able to attract. And we’re just getting started here, right? I’ve been in this role for 6, 7 months on a full-time basis. And so I think it bodes very well for the future. We want to carry on doing what we’ve done in the last 2 or 3 quarters — in the next 2 or 3 quarters and the next 20 or 30 quarters.
The reality is, I think people tend to underestimate how much progress we are making on a monthly, quarterly and annual basis. They tend to underestimate the progress that quantum computing at IonQ is making because of the double exponential nature of improvements in every generation. And they underestimate the need for quantum networking because of the threats, if you will, from not just bad state actors in a classical sense, but because there are bad state actors that are working on so-called Q-Day and cracking RSA2048. And so both sides of our business on the ground and up in space are poised, I think, to have inflection points in the coming quarters and years.
And so we’re in the early ages and era, if you will, of the quantum revolution, which is the biggest revolution in computing and networking, I think, since computer networking got going, 80 years ago. With our closed and proposed acquisition and well-fortified balance sheet, we believe we have a clear path to millions and eventually tens of millions of qubits, leading to computing power previously unimaginable from a classical standpoint. Join us now and be the first to gain commercial advantage in your industry by leveraging the massive power of our quantum networks and computers.
Niccolo McCleod Di Masi, CEO, IonQ, Q2 2025, 6 August 2025



